Images are required to remove artefacts and be processed with multiple algorithms for different purposes such as achieving different phases or individual particles.
Fei W, Narsilio GA, Disfani MM. Impact of three-dimensional sphericity and roundness on heat transfer in granular materials. Powder Technology 2019, 355:770-781, doi.
CT artefacts
CT images directly achieved in the field may have artefacts including ring artefact, noise, beam hardening, scatter, metal artefact, pseudo-enhancement, cone beam and motion etc. . Ring artefact and noise are two common artefacts in the CT images from granular materials in this study.
The ring artefacts in CT images may be induced by miscalibration and defective detector, or impurities on scintillator screens. Recalibrate or replace the detector in the filed can avoid the artefact in a new scanning. Alternatively, since the ring artefacts are strips in sinogram,it can be removed by applying Fourier filter with a Gaussian filter to the achieved images in the polar system .
Poisson noise may exist when a sample is exposed to a low dose of CT. It can be smoothed out using model-based iterative reconstruction (MBIR) while keeping the edges of solids sharp. Salt and pepper noise may exist in good quality CT images. They can be removed using the median filter resulting in non-Gaussian noises and sharp edges. Non-local means filter is another option and has a better performance for small particles but is not as effective as the median filter .
Threshold segmentation
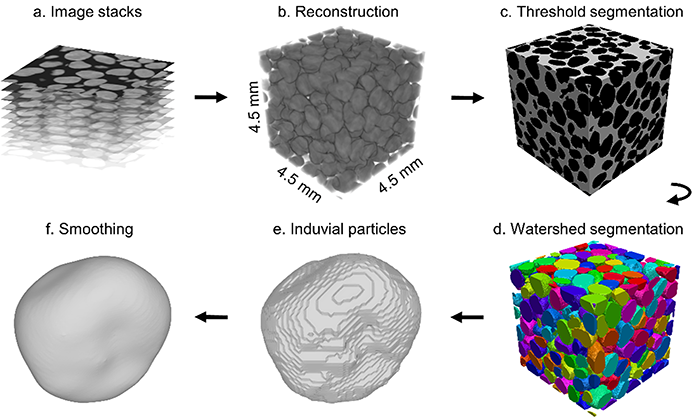
As different phases have different densities which render the corresponding voxels in contrasting grayscale. Based on the intensity levels of the grayscale, threshold segmentation can be implemented to binarize the images and separate the phases. Various thresholding algorithms were reviewed in and classified into: global and local thresholding, level sets, region growing methods, probabilistic clustering and Bayesian methods. Local thresholding methods can generate satisfactory results, but they are sensitive to initial inputs. Otsu and Rilder are two global thresholding algorithms that are adequate to segment different phases. The connectivity or neighbourhood between voxels also needs to be specified when applying a threshold segmentation. In 3D, 6-, 18- or 26-connectivity of a voxel is related to common face, edge or vertex. 6-connectivity can reduce the overestimation of particle surface area or contact area while 26-connectivity benefits the identification of particle boundaries .
Images are required to remove artefacts and be processed with multiple algorithms for different purposes such as achieving different phases or individual particles.
Segmentation of Aggregates
After identifying solid phases, aggregates in non-destructive samples need to be segmented to obtain discrete particles to calculate particle size and shape. The watershed algorithm is a popular choice to complete this task. It uses a topographic analogy on greyscale images or distance map . A distance map is generated from a binary image which can be achieved after threshold segmentation. Then each pixel in the solid is assigned with a new grayscale whose value is equal to the distance from the pixel to the nearest background pixel. The greyscales are considered as altitudes such that an image can be converted to topographic surface. From each minimum region (i.e. local minima on greyscale images or distance maps), water is flooded, and dams are created at where the water from different valleys meet to find different catchment basin. The watersheds are the zones dividing neighbouring catchment basins.
The classic watershed algorithm works best for smooth convex objects without large overlap . It may lead to overestimation if too many local minima are found due to noise in the images. Filters such as Gaussian and median filter are recommended to remove the noise. A plugin named MorphoLibJ also offers the option to merge over-segmented regions. Other minima such as extended minima can also be generated using other algorithms or selected manually to replace the local minima in classic watershed segmentation. Additionally, Canny edges created based on the gradients of CT images can represent particle boundaries and be used to check the validity of watersheds .
As an alternative to the watershed algorithm, a machine learning tool named Trainable Weka Segmentation was developed. It is a voxel-based algorithm and generates possibility maps indicating which class each voxel belongs to. Hence, if the classes are trained for only solid and void phase, it can binarize the images as threshold segmentation does. It can also segment different objects if voxels are marked into different classes during training.
Please cite our papers below related to CT imaging
- Fei W, Narsilio GA. Impact of Three-Dimensional Sphericity and Roundness on Coordination Number. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering 2020, 146:06020025, doi.
- Fei W, Narsilio GA. Network analysis of heat transfer in sands. Computers and Geotechnics 2020, 127:103773, doi.
- Fei W, Narsilio GA, van der Linden JH, Disfani MM. Quantifying the impact of rigid interparticle structures on heat transfer in granular materials using networks. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer 2019, 143:118514, doi.
- Fei W, Narsilio GA, Disfani MM. Impact of three-dimensional sphericity and roundness on heat transfer in granular materials. Powder Technology 2019, 355:770-781, doi.
